Guidelines & Procedures For Country Assistance Programmes (CAPS)

Overview of Country Assistance Programmes (CAPs)
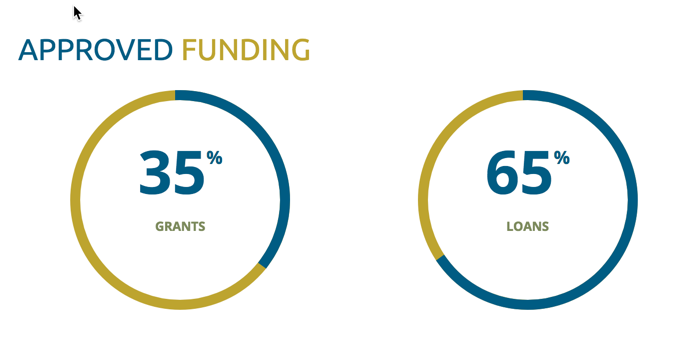
The CDF provides loans, grants and technical assistance to the public and private sectors of Member States to:
- address adverse economic and social impacts arising from the implementation of CSME;
- attract investment and new industries to disadvantaged countries, regions and sectors;
- improve efficiency and competitiveness of industry; and
- achieve structural diversification and infrastructural development.
In 2011, the CDF adopted a Country Programming Approach, whereby assistance is provided to distinct development components and projects within an overall Country Assistance Programme (CAP). CAPs must be clearly linked to improving trade competitiveness in regional and extra regional markets, for example:
- Policy reviews and recommendations;
- Business diagnostics and implementation of turn-around strategies;
- Standards improvements and certifications such as ISO, HACCP and similar compliance with best practices in production and marketing;
- Business and investment promotion and special measures to attract investment and new industries to the disadvantaged counties and regions;
- Amelioration of production and trade dislocations arising from the introduction of the Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) with the European Union (EU);
- Skills training for productivity improvement; and,
- Emergency response to trade related dislocation (a temporary interruption) arising from natural disaster.
The following types of activities are not eligible for CDF financing:
- Major infrastructure projects requiring the injection of significant capital (unless the project is co-finance from other sources);
- Complex programmes with multiple goals;
- Open ended budgetary and balance of payments support for Member Countries;
- Re-financing activities for sunset industries and for debt consolidation that does not create new or improved productive capacity; and Working capital.
CDF’s focus areas are subject to change at the beginning of Contribution and Subvention Cycles depending on the assessed and agreed priorities of CDF Member States. All CDF Member States are eligible to receive financial and technical assistance from the Fund during a Contribution and Subvention Cycle. The First Contribution Cycle (July 2008 – December 2015) focused on the programming needs of Less Developed Countries (LDCs) and Guyana (classified as a Highly Indebted Poor Country (HIPC)), in recognition of their special status and needs. The current Second Cycle is focused on addressing disparities that cause constraints to the full implementation of the CSM by disadvantaged countries and specifically emphasizing:
- Building human capacity;
- Business development and enterprise competitiveness to increase trade in goods/services (the private sector);
- Sustainable Energy;
- Specific Infrastructure to support trade and investment; and,
- Creating regulatory and administrative systems where gaps exist and establishing/ strengthening domestic institutions.
In order to determine the priorities of a particular Subvention Cycle, the CDF undertakes extensive consultations within and among Member States and the Regional Institutions Secretariats. The Regional Development Division of the CDF (RDD) reviews data and conducts meetings with representatives of Member State governments and key stakeholders in economic development to determine how CDF can facilitate the convergence of CSME and national agendas. These consultations are documented and analysed by the RDD and reviewed internally by the Senior Management and Specialist staff to arrive at recommendations on priorities for the cycle. This process normally commences in June of the year preceding the end of the Cycle. The Chief Executive Officer of the CDF presents the proposed Subvention Cycle priorities for CDF Board approval and subsequent confirmation of the approval by CARICOM Council of Ministers for Trade and Economic Development (COTED), CARICOM Council of Ministers for Finance and Planning (COFAP) and the Community Council. Prior to the completion of the funding Cycle, and upon final approval, CDF advises Member States of the priorities of the new Subsequent Cycle. The RDD conducts Country Missions to generate activity toward the development of Country Assistance Programmes (CAPS).
A Member State meeting the conditionalities of the Subvention Cycle and wishing to access CDF support prepares a CAP that identifies the broad objectives to be met, types of activities to be funded and approximate funding envelope required. Once approved, the Member State works with CDF to design discrete activities in Components and or Projects within the CAP. Public and private sector entities in all CDF Member Countries are eligible to apply for CDF and receive financial and technical assistance once the following conditions have been met by the Member State:
- The Member State’s development priorities must be consistent with the objectives of CSME and the priorities of the current CDF Subvention Cycle;
- The Member State must be committed to those priorities;
- The National Focal Point (NFP) must be in place to serve as the local agent of the CDF; and,
- The Member State must have a formal Agreement in place with the CDF based on an approved CAP Summary.
Private sector entities are eligible to apply for CDF loan financing through an approved financial intermediary in country, e.g., a national development bank or other financial intermediary, as identified by the CDF in the respective country.